Domain Trust Exploitation refers to the abuse of trust relationships between domains within a network, often within environments using Active Directory (AD). In these environments, domains can establish trust relationships to allow users in one domain to access resources in another. While these trusts are necessary for managing access in large networks, they can be exploited if not properly secured.
Core Concept of Domain Trust Exploitation
Trust Relationships:
Trusts are connections established between domains to allow shared access to resources. They can be:
Types of Domain Trusts in Active Directory
In Active Directory, domain trusts are relationships established between domains to allow access to resources across them. Here are the main types of domain trusts:
How does it work?
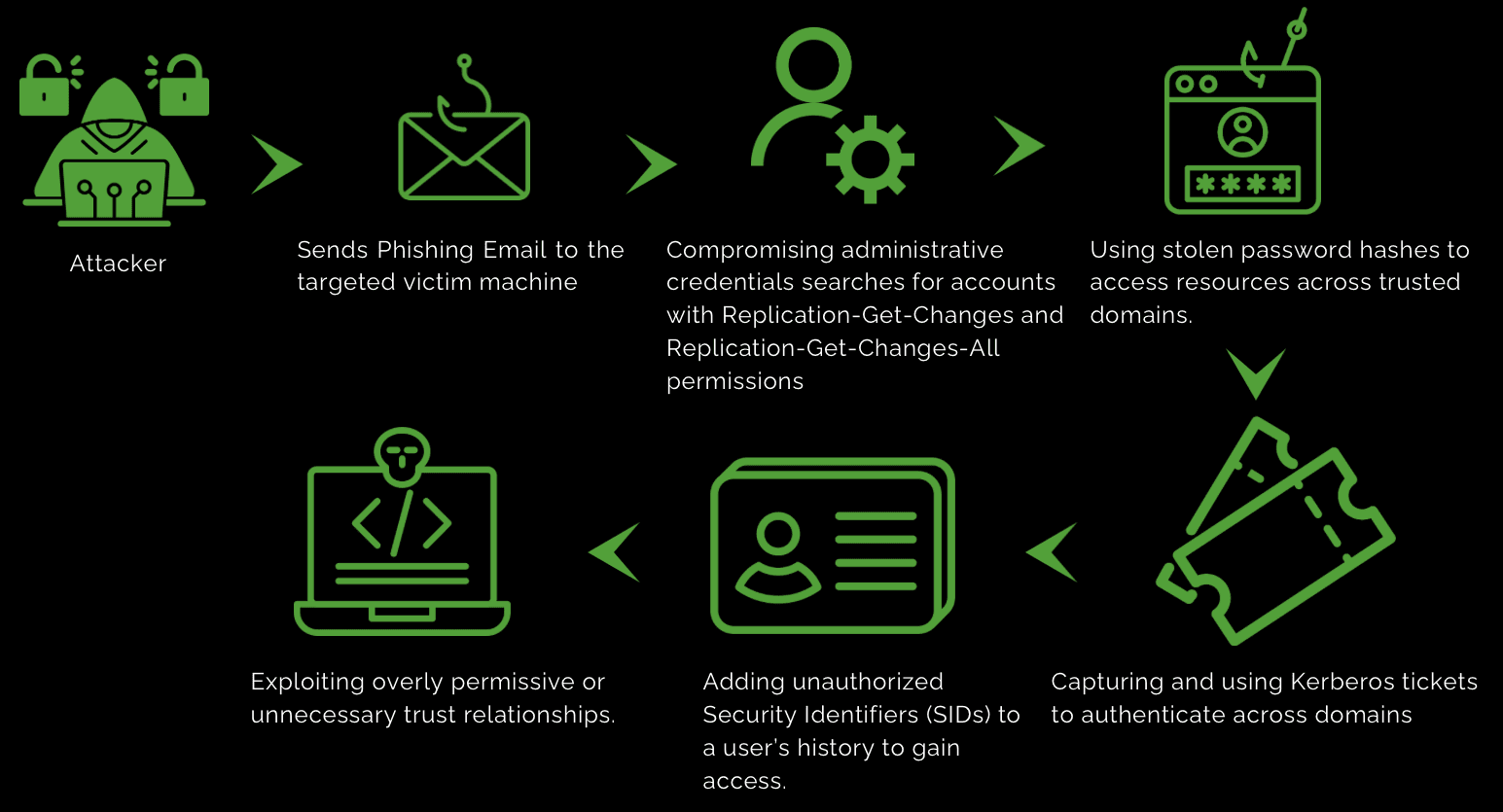
Exploitation methods for domain trusts involve various techniques that attackers use to abuse trust relationships between domains in an Active Directory environment.
One prevalent method is Pass-the-Hash (PtH), where attackers capture and reuse hashed password values (NTLM hashes) to authenticate across trusted domains. Another technique, Pass-the-Ticket (PtT), involves capturing and reusing Kerberos tickets to gain unauthorized access to resources in different domains.
SID History Injection allows attackers to insert unauthorized Security Identifiers (SIDs) into a user’s SID history, providing access to resources in trusted domains. Kerberoasting involves requesting and cracking service tickets for service accounts to obtain passwords.
Silver Ticket attacks enable attackers to forge Kerberos service tickets for accessing specific services, while Golden Ticket attacks involve forging Ticket Granting Tickets (TGTs), which grant extensive privileges and access across all domains within a forest. These methods underscore the critical need to secure domain trusts and monitor for unusual activities to prevent such attacks.
Happy Learning !!