Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) phishing attacks are a highly sophisticated and increasingly common form of cyberattack that allows attackers to bypass traditional security measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA). Unlike conventional phishing attacks, which rely on tricking victims into revealing their login credentials, AiTM attacks enable cybercriminals to intercept and manipulate real-time communications between the user and the legitimate service. This makes AiTM attacks harder to detect and mitigate, significantly increasing their potential impact on both individuals and organizations.
In this blog, we'll dissect the infection chain of an AiTM phishing attack, explaining how it works and how attackers use this advanced strategy to exploit their victims. We'll also include a flow diagram to help visualize the attack process, making it easier to understand how each step unfolds.
The AiTM Phishing Infection Chain
This attack begins with a compromised trusted vendor, which served as the entry point for a series of AiTM phishing attacks and subsequent Business Email Compromise (BEC) activity across multiple organizations. The attack highlights the complexity of AiTM and BEC threats, which exploit established, trusted relationships between vendors, suppliers, and partner organizations with the goal of committing financial fraud.
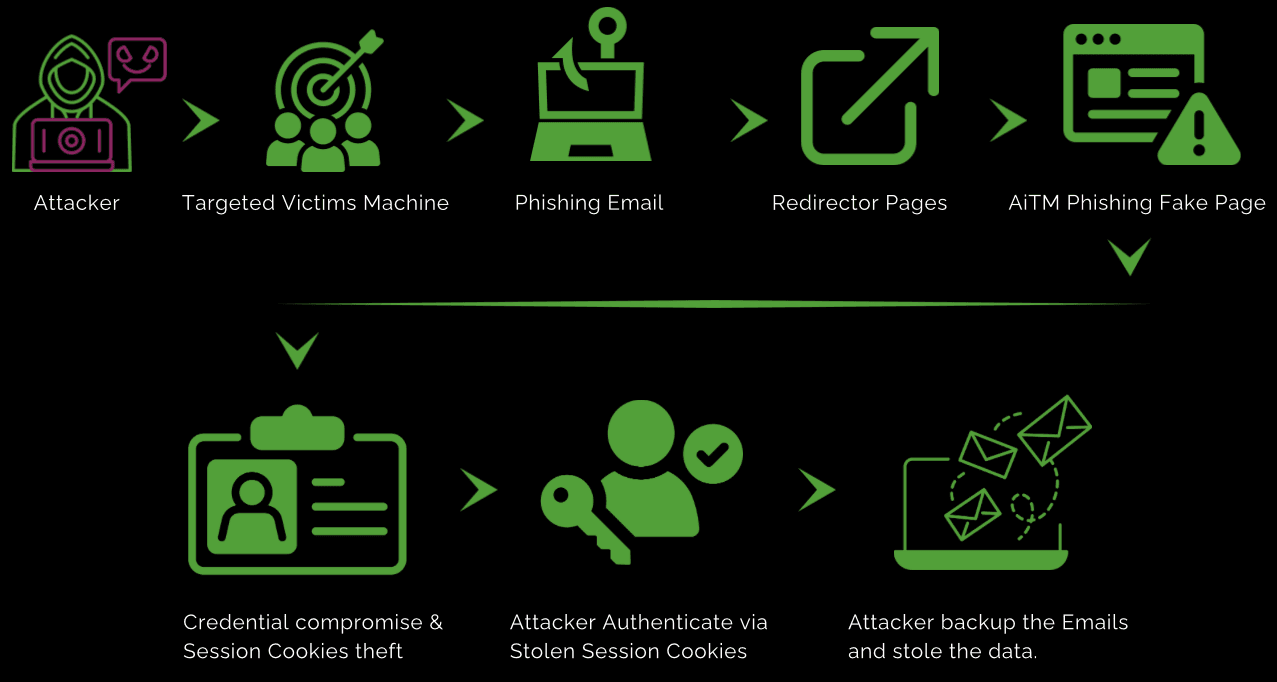
Below is a breakdown of each stage in the infection chain:
1. Initial Phishing Email
The attack begins with a targeted phishing email that convinces the victim to click on a malicious link. The email often appears to come from a trusted source, such as a bank, email provider, or cloud service. It typically uses urgent language (e.g., "account suspended" or "unauthorized login attempt") to prompt immediate action from the victim.
2. Redirect to Fake Login Page
The phishing email contains a link that redirects the victim to a counterfeit login page designed to look identical to the legitimate service. Once the victim clicks on the link, they are directed to this fake site, where they are asked to enter their login credentials.
3. Credential Harvesting
When the victim enters their login credentials, including username and password, the attacker collects this information. However, the attacker doesn’t just steal the victim's basic login details—they may also capture session cookies or authentication tokens. These session credentials can be used to hijack the victim’s ongoing session with the legitimate service.
4. Session Hijacking and Real-Time Proxying
Positioned "in the middle" of the victim's interaction, the attacker forwards the stolen login credentials to the legitimate service in real-time. Additionally, the attacker uses the intercepted session cookies or tokens to maintain access to the victim's account. Since the attack is seamless, the victim doesn’t notice any disruption, making it difficult for them to detect the intrusion.
5. Exploiting the Compromised Account
Once the attacker successfully gains access to the account, they can exploit it for various malicious purposes. This could include stealing sensitive data, conducting fraudulent transactions, or even launching additional attacks against other users or organizations.
6. Covering Tracks and Ensuring Persistence
After exploiting the account, the attacker may take steps to cover their tracks, such as deleting logs or altering security settings to avoid detection. In some cases, the attacker ensures they can maintain persistent access to the compromised account, allowing them to continue their malicious activities without being discovered.
How to Protect Against AiTM Phishing Attacks?
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) with Stronger Protections.
Implement Web Filtering and Email Security Solutions.
Monitor Login Activity for Anomalies.
Encourage Strong Password Hygiene.
Use Anti-Phishing Software.
Conclusion:
AiTM phishing attacks represent a sophisticated and highly effective form of cyberattack that targets both users and the authentication process itself. By sitting between the user and the legitimate service, attackers can steal credentials, bypass MFA, and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Recognizing the infection chain and implementing a multi-layered defense strategy are essential steps in mitigating the risk of AiTM attacks.
Staying vigilant and proactively defending against AiTM attacks!!
Happy Reading !!


