AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a cloud computing platform from Amazon that offers a wide range of on-demand services, including computing power, storage, databases, and machine learning. It enables businesses and developers to access these resources remotely, eliminating the need for physical hardware. With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, AWS provides scalable and cost-effective solutions for organizations of all sizes.
In this blog, we'll guide you through the process of signing up for AWS and using the AWS Management Console, step by step.
Step 1: Sign Up for AWS
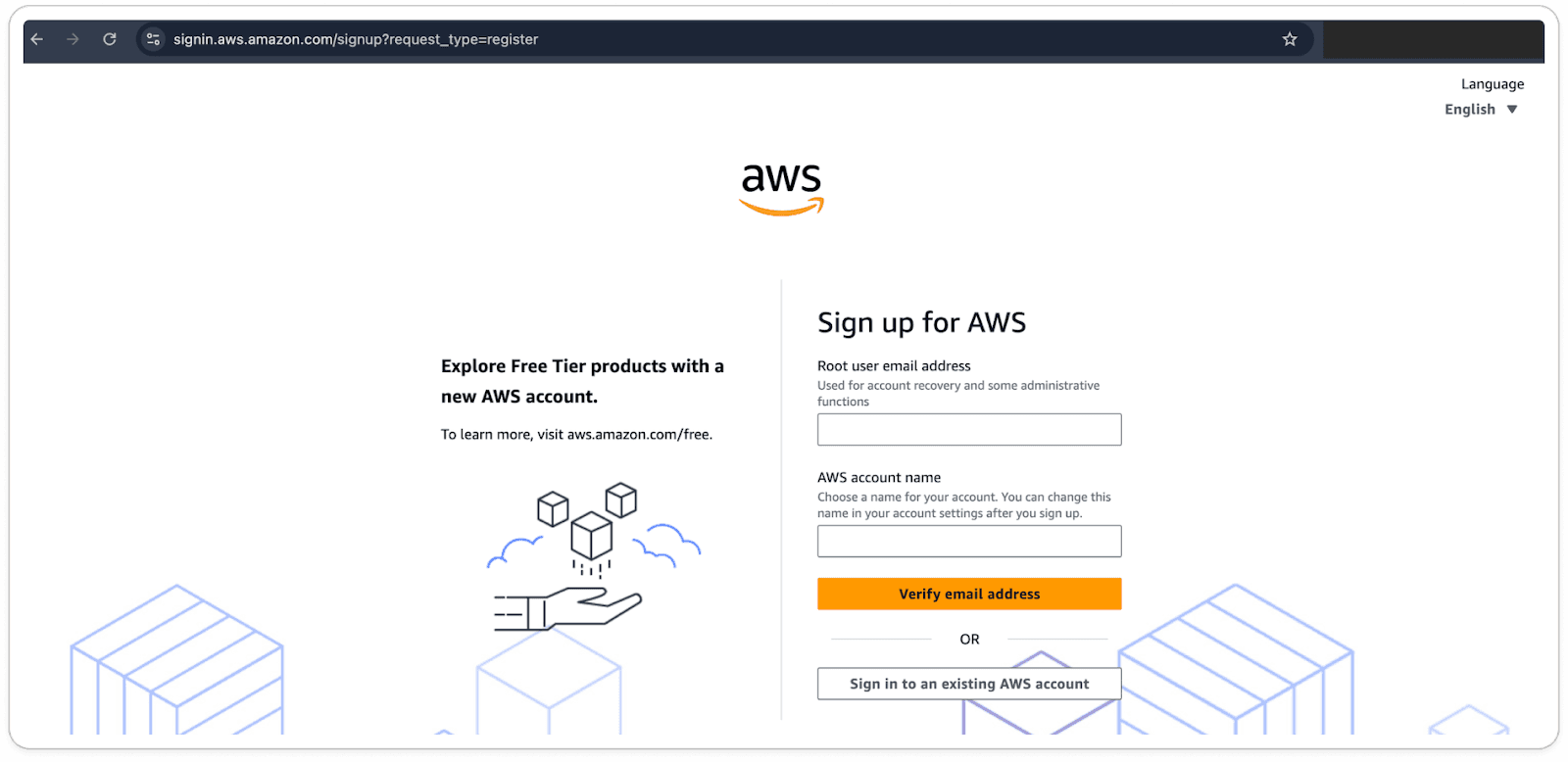
Go to the AWS Homepage and Visit AWS’s sign-up page in your browser.
In the top-right corner of the homepage, click on the "Create a Free Account" button.
Provide Your Email, Password, and AWS Account Name.
Choose an AWS Support Plan.
Enter Your Payment Information.
Identity Verification (via Phone).
Select Your AWS Region.
Complete the Registration.
Once all steps are completed, AWS will send you a confirmation email. Click the link in the email to finalize your sign-up.
Step 2: Log In to AWS Management Console
Once you have completed the sign-up process, you can log in to the AWS Management Console, where you can manage and configure AWS resources.
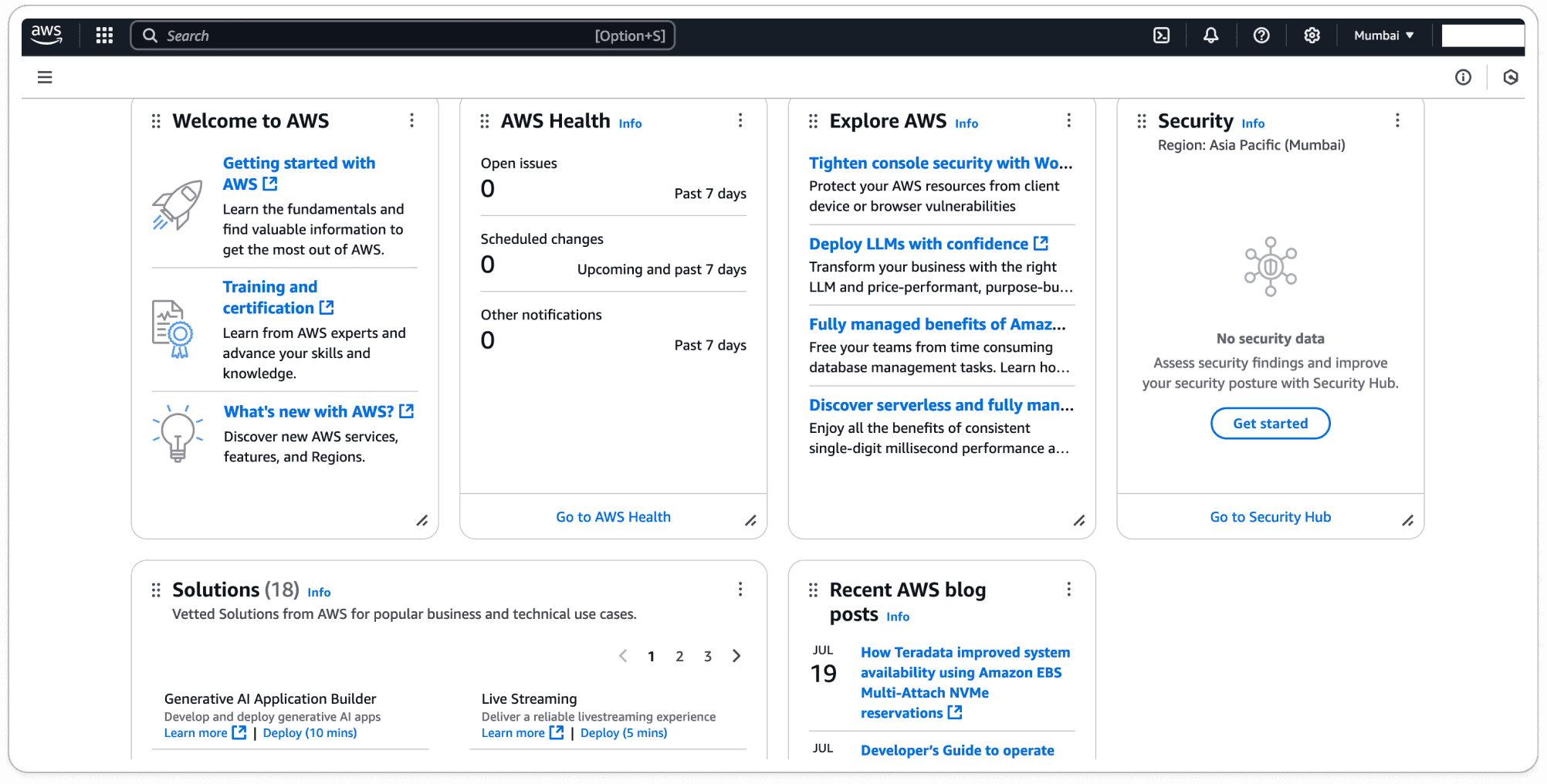
Step 3: Explore the AWS Management Console
Once you're logged into the AWS Management Console, you’ll have access to a wide variety of AWS services. AWS offers over 200 services that cover everything from computing and storage to machine learning, security, and analytics.
The console provides an intuitive interface to help you navigate and manage these services. Whether you're launching a virtual machine with EC2, setting up storage with S3, or building a database with RDS, the AWS Management Console gives you the tools you need to configure and monitor your cloud resources.
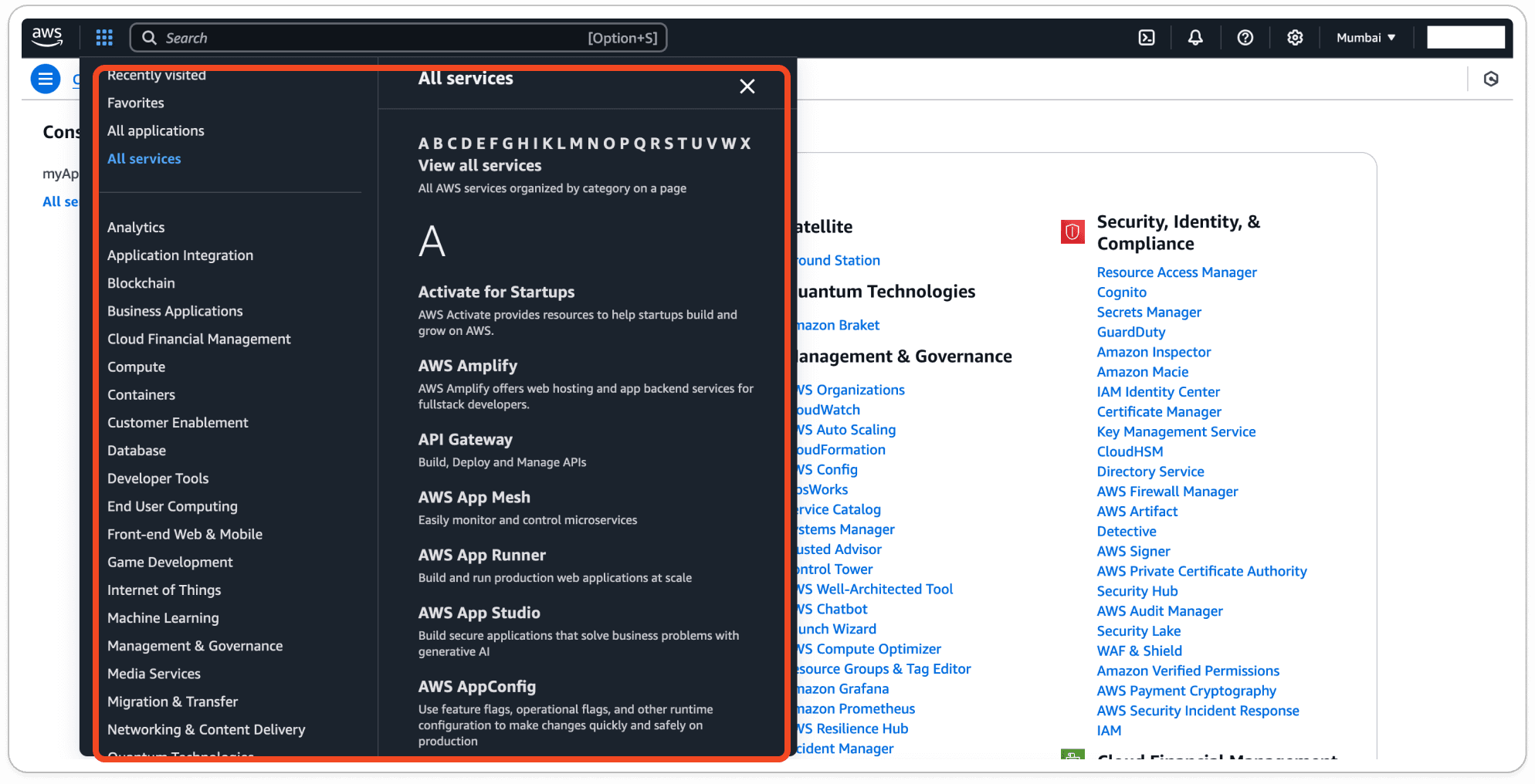
Here’s a quick overview of some key service categories available in the console:
Compute Services – Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), AWS Lambda, Amazon Lightsail, Amazon Elastic Beanstalk, AWS Batch.
Storage Services – Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service), Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store), Amazon Glacier, Amazon FSx, AWS Storage Gateway.
Database Services – Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service), Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Aurora, Amazon ElastiCache, Amazon Neptune.
Networking & Content Delivery – Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), Amazon CloudFront, AWS Direct Connect, Elastic Load Balancing, Amazon Route 53.
Security & Identity – AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management), AWS KMS (Key Management Service), AWS Shield, AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall), AWS Secrets Manager.
Machine Learning & AI – Amazon SageMaker, AWS Rekognition, Amazon Lex, Amazon Polly, AWS Comprehend, Amazon Transcribe.
Analytics – Amazon Redshift, Amazon Athena, Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce), AWS Glue, Amazon QuickSight, AWS Data Pipeline.
Developer Tools – AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeCommit, AWS CodeBuild, AWS CodeDeploy, AWS Cloud9.
Internet of Things (IoT) – AWS IoT Core, AWS IoT Greengrass, AWS IoT Device Defender, AWS IoT Analytics, AWS IoT Things Graph.
Migration & Transfer – AWS Migration Hub, AWS Server Migration Service (SMS), AWS Database Migration Service (DMS), AWS Snowball.
Business Applications – Amazon WorkSpaces, Amazon Chime, Amazon WorkDocs, Amazon WorkMail.
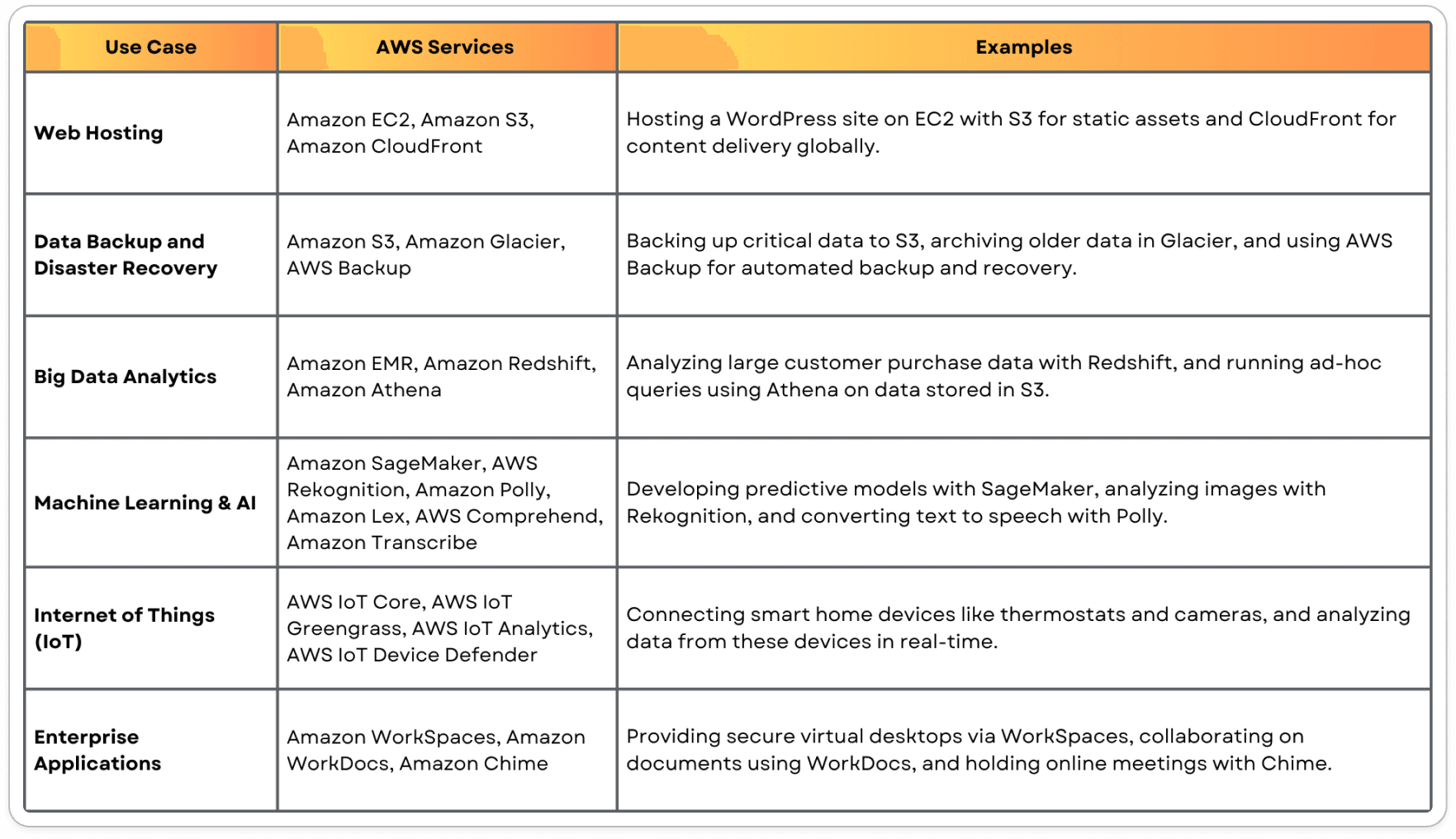
Use Cases of AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a wide range of cloud solutions that can be utilized across different industries and use cases. Below are some of the most popular and impactful ways AWS is being leveraged today:
Conclusion
AWS is a robust cloud platform that empowers businesses and developers to innovate quickly and efficiently. If you're new to AWS, the Practical 101 Series is an ideal starting point for your cloud journey.
In our upcoming blogs, we’ll dive deeper into each of these AWS resources, offering detailed explanations, use cases, and hands-on tutorials to help you get the most out of AWS. Stay tuned for more practical insights to guide you through your AWS journey!
Happy Learning!!