In today’s digital landscape, cloud computing has become a cornerstone of business operations, no longer just a passing trend. Companies of all sizes, whether startups or Fortune 500 giants are moving their data, applications, and services to the cloud to boost efficiency, scalability, and flexibility. However, with the rapid adoption of cloud technologies comes an increase in the security challenges that organizations must address.
In this blog, we’ll break down the fundamentals of cloud security, why it’s so important, and the essential steps you need to take to protect your cloud environment.
What Is Cloud Security?
Cloud security refers to a set of practices, policies, and tools designed to safeguard cloud-based systems, data, and applications. This includes everything from securing physical infrastructure at data centers to managing access controls and encryption for data in transit and at rest.
Unlike traditional on-premise IT infrastructure, where organizations have full control over physical hardware and network configurations, cloud environments introduce new complexities. The key challenge is securing your data and applications when they are hosted offsite, often on shared infrastructure, and accessed from various locations by employees, customers, and partners.
Why Is Cloud Security Important?
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud technologies, securing the cloud environment becomes a must. Let’s look at some key reasons why cloud security should be top of mind:
Protecting Sensitive Data
Many organizations store valuable and sensitive data such as customer information, financial records, and intellectual property—in the cloud. Without adequate security measures, this data is vulnerable to theft, leaks, or loss.
Compliance Requirements
Depending on the industry, businesses may need to meet various compliance regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, which set stringent rules for data protection. Cloud security plays a crucial role in helping organizations remain compliant with these regulations.
Minimizing Business Risk
A data breach or security incident can lead to severe financial, reputational, and operational damage. Strong cloud security helps mitigate risks and ensures business continuity by preventing security incidents before they happen.
Cloud Security Architecture:
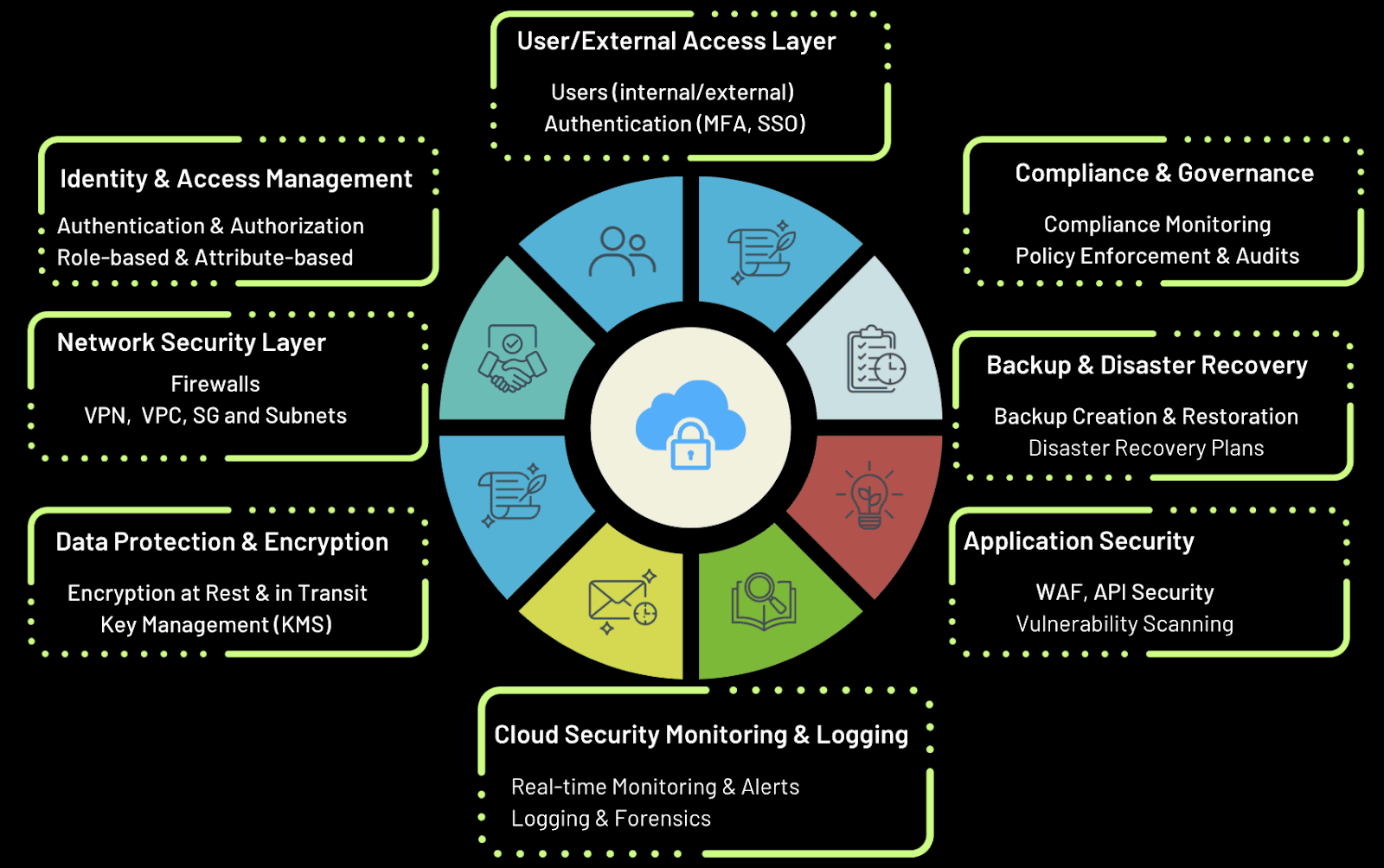
What is a Shared Responsibility Model?
One of the most critical aspects of cloud security is understanding the Shared Responsibility Model. Cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud operate on the premise that both the provider and the customer share security duties though their responsibilities are divided.
Provider’s Responsibility:
Cloud providers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, including physical data centers, hardware, and networking components. They also ensure the security of the platform’s core services (e.g., compute, storage, and networking).
Customer’s Responsibility:
Customers (you) are responsible for securing the data, applications, and user access in the cloud. This includes tasks like configuring access controls, ensuring data encryption, managing user identities, and implementing security best practices.
Understanding this model is crucial because it means that while cloud providers handle physical infrastructure security, the customer is accountable for securing their data and ensuring proper configurations are in place.
Key Cloud Security Principles
There are several fundamental principles that should guide any cloud security strategy. These principles help ensure your cloud environment is secure, resilient, and well-protected against threats.
Data Encryption
Protecting data is one of the top priorities in cloud security. Encryption ensures that your data is unreadable to unauthorized users, even if it is intercepted or accessed.
At Rest: Encryption of stored data ensures it’s secure when not in use.
In Transit: Encryption during transmission protects data as it moves between endpoints, preventing interception or manipulation.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Managing user access is crucial to minimizing risks. With strong IAM policies, you can enforce:
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Limit access based on job roles, ensuring users only have access to the resources they need.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance access security by requiring multiple verification methods to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
Continuous Monitoring
Cloud environments are dynamic, and constant monitoring is essential to identify and respond to security threats in real time. Monitoring helps track access, detect abnormal activities, and ensure that security controls are working as expected.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data loss can happen for various reasons, from system failure to cyberattacks. Regular backups and a well-defined disaster recovery plan ensure that your cloud-based data can be quickly restored, minimizing downtime and operational impact.
Security Configuration
Misconfigurations are one of the leading causes of cloud security incidents. Ensuring that your cloud services and resources are securely configured—such as restricting open storage buckets, properly setting access control policies, and disabling unused services—helps prevent security vulnerabilities.
Challenges in Cloud Security
While cloud computing offers many advantages, it also presents unique security challenges. Here are a few of the most common obstacles businesses face when securing their cloud environments:
Data Privacy and Sovereignty
Storing data in the cloud means it might be hosted in different regions or countries, which introduces concerns about data privacy and legal compliance. Organizations need to be aware of data protection laws in the regions where their data resides.
Expanding Attack Surface
Cloud environments are highly interconnected, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Each service, API, or endpoint represents a potential vulnerability that attackers can exploit if left unsecured.
Insider Threats
Employees or contractors who have legitimate access to your cloud environment could intentionally or unintentionally compromise security. Implementing strong access controls and monitoring for unusual activity can help minimize these risks.
Lack of Visibility
Unlike on-premise infrastructure, cloud environments often limit the visibility IT teams have over the physical hardware. This can make it more challenging to track and manage security risks, especially if you are using multiple cloud providers.
Conclusion
As businesses continue to embrace cloud technologies, ensuring robust cloud security is more important than ever. By understanding the shared responsibility model, following key security principles, and adhering to best practices, you can build a secure and resilient cloud infrastructure that protects your data, complies with regulations, and safeguards your reputation.
While cloud security can seem daunting, a proactive and well-informed approach will help you stay ahead of potential risks and make the most of the benefits that the cloud has to offer.
Happy Learning !!